





还剩32页未读,
继续阅读
外研版八年级英语下册Module3课件
展开
这是一份外研版八年级英语下册Module3课件,共40页。
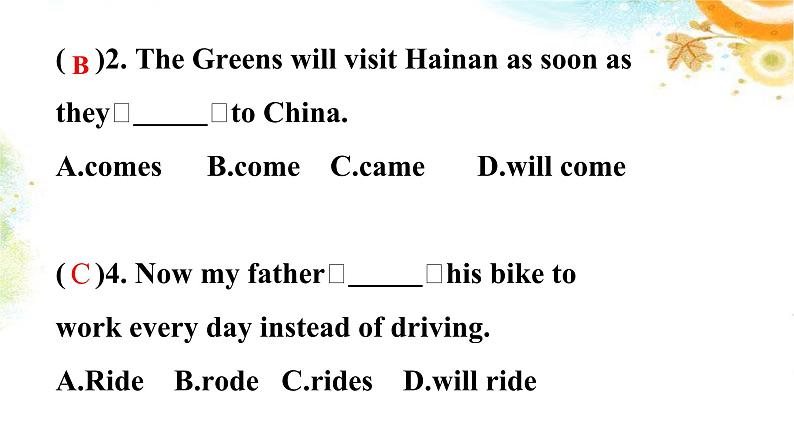
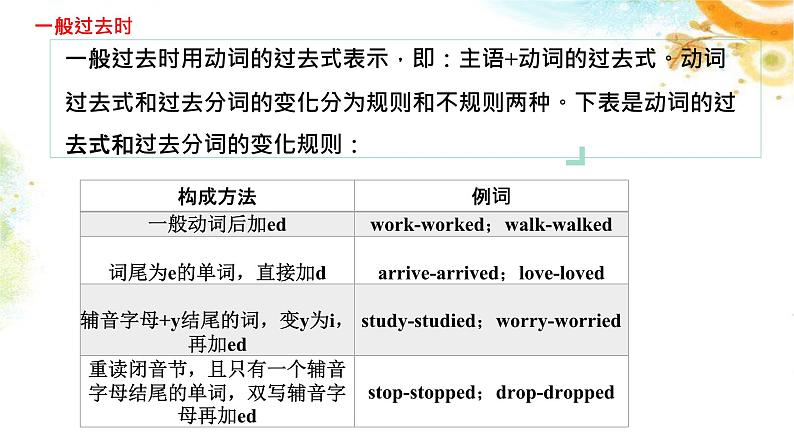
时态讲解一般现在时主要用动词原形表示,如果主语是第三人称单数则在动词原形后加s或es。动词第三人称单数的构成方式如下: 一般现在时经常性或习惯性的动作或状态考点突破客观事实或普遍真理The earth goes around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。主将从现(时间、条件、让步)If it rains tomorrow,we won’t/ will not go to the park. When I grow up,I will go to America.Although he is 14 years old, he will join the army. 常与often,always总是,usually,sometimes,once a week,every day等表示频率的副词或时间状语连用。如:I often go to school by bike. ( )1. If Nancy the exam,she will go to Australia for English study. A.pass B.passed C.passes D.will pass ( )3. — I don’t know if Mr.Li to the party this evening. —I think he will come if he free. A.will come; is B.will come; will be C.comes; is D.comes; will beC A( )2. The Greens will visit Hainan as soon as they to China. A.comes B.come C.came D.will come( )4. Now my father his bike to work every day instead of driving. A.Ride B.rode C.rides D.will rideBC一般过去时用动词的过去式表示,即:主语+动词的过去式。动词过去式和过去分词的变化分为规则和不规则两种。下表是动词的过去式和过去分词的变化规则:一般过去时过去发生的动作或存在的状态考点突破常与last night昨晚,yesterday,last week上周,some years ago,in 1995,in the past在过去,the other day几天以前,at that time, 在那时候,在那个时刻,just now等表示过去的时间状语连用。如: I got up at six yesterday. 过去的习惯或经常发生的动作When I was in the countryside乡下,I often swam in the river.主句现在完成时,since从句一般过去时He has worked in the factory since it opened in 1990.You haven’t changed much since we last met.grow -- grewknow -- knewthrow -- threwblow -- blewwrite -- wrotedrive -- drove ride -- rodeget -- gotforget -- forgotlend -- lentsend -- sentspend -- spentsay -- said pay -- paidstand -- stoodunderstand – understood明白let -- let put -- putcut -- cut read -- read*am, is -- was are -- were do -- did go -- went have -- hadsee -- sawcan -- couldmay -- mightdig – dug挖掘eat -- atefind -- foundmake -- madehear -- heardrun -- rantake -- tookhold – held举行,拿着speak -- spokeleave -- leftkeep -- keptsleep -- sleptsweep -- swepttell -- toldsell -- soldbegin -- begansing -- sangsit -- satswim -- swamring -- ranggive -- gave bring -- broughtbuy -- boughtthink -- thoughtteach -- taughtcatch -- caughtcome -- came become -- became ( ) 1. Our math teacher in our school for 20 years and he_____ here when he was 23 years old. A.has taught;has come B.taught;comes C.taught;came D.has taught;came ( ) 2. — You have found your lost umbrella, haven’t you? —Yes.I it behind the door this afternoon. A.have found B.will find C.found D.find DC一般将来时通常用“主语+will/ shall/be going to+动词原形”来表示,有些动词可以用“主语+be doing”形式来表示。 一般将来时肯定句:主语 + will / shall + 动词原形否定句:主语 + will / shall not + 动词原形一般疑问句:Will + 主语 +动词原形?特殊疑问句:W、H开头特殊疑问词 +一般疑问句?肯定/否定回答: Yes,主语+will. /No,主语+will not.will not=won’t将来发生的动作或存在的状态考点突破常与tomorrow,next week,in a few days(在一些天以内),next Sunday等表示将来的时间状语连用。如:Will you be back in two days?be going to+动词原形,表示打算做某事,常指已经决定的、很可能发生的事或有某种迹象表明要发生的事What are you going to do next Sunday? be doing也可表示即将发生或安排好要做的事情常用这种结构的动词有:go,come,leave,arrive,start,begin等。如:She is going there tomorrow.详写内容……点击输入本栏的具体文字,简明扼要的说明分项内容,此为概念图解,请根据您的具体内容酌情修改。详写内容……点击输入本栏的具体文字,简明扼要的说明分项内容,此为概念图解,请根据您的具体内容酌情修改。点击输入内容点击输入内容易错点:There be 句型的一般将来时There will beThere won’t beWill there be…?Yes,there will.No,there will not.There is/are going to beThere is/are not going to beIs/Are there going to be…?Yes,there is/are.No,there is/are not.There will be a football match tomorrow.There is going to be a football match tomorrow.( )1. —Let’s go fishing if it this weekend. —But nobody knows if it . A.is fine;will rain B.will be fine;rains C.will be fine;will rain D.is fine;rains ( )2. If there is any change to the plan, I you as soon as possible. A.told B.have told C.tell D.will tell AD现在进行时的构成为:主语+be(am/is/are)+动词的现在分词。动词的现在分词和动名词的变化规则如下表: 现在进行时表示此时此刻正在进行的动作考点突破—What are you doing? 你在干什么? —I’m reading English. 我在读英语。表示现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态I’m reading books these day.while从句动词通常要用进行时While you are sitting on the grass,I’ll read you the novel.现在进行表将来come, go,leave,arrive,start等动词用现在进行时表示将来。如:The bus is coming soon. ( ) 1. Don’t disturb Allen now. He _____ for the Spelling Bee competition.A.prepares B.prepared C.is preparing D.will prepare( )4. Be quiet ! The students _____ a physics test in the next room.A.had B.have had C.were having D.are having CD( )2. —Alan,it’s late.Why not go to bed? —Jenny hasn’t come back yet.I for her. A.waited B.have waited C.am waiting D.was waiting ( )5. Listen! The phone .Please go to answer it. A.rings B.is ringing C.rang D.will ringCB( )3. —Jackson,I haven’t seen you these days. —I for the coming English test. A.am preparing B.will prepare C.prepare D.have prepared ( )6. —Where’s your mother,Jack? — She’s gone to the supermaket.I think she now. A.shops B.will shop C.shopped D.is shoppingAD2.过去进行时的用法 (1)表示在过去的某个时刻、正在进行的动作或存在的状态或过去某段时间一直做的动作,常与this time yesterday,at that time,at 9:00 last Sunday morning,all night等表示过去的时间状语连用。如: —What were you doing this time yesterday? 昨天的这个时候你在做什么? —I was watching TV. 我在看电视。 过去进行时1.过去进行时的构成 过去进行时的构成为:主语+be(was/were)+doing过去进行时。 (2)表示一个过去的动作发生时或发生后,另一个过去的动作正在进行。过去进行时也可用来表示过去一段时间内持续发生的动作。如:When I was watering the garden,it began to rain. While we were having a party,the lights went out. (3)表示两个过去的动作同时进行,这时可用连接词while连接。如: I was writing while my mother was cooking.George was reading while his wife was listening to the radio. (4)“was going+动词不定式”表示过去打算做某事。如: He was going to be our team leader.( )1.— I didn’t see you at the beginning of the party last night. —I on my biology report at that time. A.worked B.work C.was working D.am working( )4 .— Why didn’t you go to the cinema with us this afternoon? — I at the station for my uncle from Beijing. A.was waiting B.have waited C.am waiting D.will wait CA( )2. Jenny in the kitchen when you called her at 5 o’clock this afternoon. A.is cooking B.was cooking C.cooks D.cooked( )5. — I called you at 4:00 yesterday afternoon, but no one answered. —Sorry, I with my friends at that time. A.swim B.swam C.will swim D.was swimmingBD( )3. Louis computer games when her brother phoned her. A.plays B.is playing C.has played D.was playing( )6. I was very angry with John, he just when I spoke to him. A.isn’t listening B.hasn’t listened C.didn’t listen D.wasn’t listening DD现在完成时用法:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,强调的是现在的情况。构成:助v. have/has + done否定句:haven’t / hasn’t + done一般疑问句:Have / Has sb. done…?I have... = I've You have... = You've...We have... = We've... They have... = They've...He has... = He's... She has... = She's缩写形式: have/ has + done. (过去分词)过去分词不规则变化 现在完成时 使用语境1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去We've already finished our homework.Tintin has been popular for over eighty years. have/ has + done. (过去分词)2.常用标志词: already(肯定句) yet(否定句和疑问句 句末)never(否定句)ever just before(句末)so far, these days, 1.She has not seen this film . She has seen this film.2.I have combed my hair. Have you combed your hair .3.He has watched a video. He has not watched a video . already ---------- yet 已经 用于肯定句 用于否定句,疑问句 yetalreadyalready yet yet already3.对点练习:1. I ________ (do) my homework already.2. He _____________(not finished) his homework yet.3. _______you ever ______ (be) to Haiwaii?4. We ______ never ______ (see) such an exciting match before.5.Mother _____ just _______(clean) the house. Please don’t come in.6.They _________________(practice) this dialogue twice.have donehas not finishedHavebeenhaveseenhascleanedhave practiced1. have been to +地名, “曾经去过某地”, 人已回来 They have been to Beijing twice. 2. have gone to +地点, “去了某地”, 人未回来 They have gone to Beijing. 3. have been in +地点, “在某地待了多久”,可以和时间段连用 They have been in Beijing for 10 years. 4.【特殊句型要牢记】 用have /has been to和have / has gone to have been in 填空 1.Lucy has been to the Great Wall twice. 2.— What about your sister,Lily? — Oh,she Chengdu, she will come back next week.3.The Blacks have been in China for two years. has gone to2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去现在完成时表“延续”条件一: 与“延续性时间状语”连用Tintin has been popular for over eighty years.Tintin has been popular since 1929.Tintin has been popular since over eighty years ago.Tintin has been popular since the artist invented him.“延续性时间状语”: for + 时间段 since + 时间点Have a Try: 用 for 和 since 填空__________ three minutes __________ a week__________ two o'clock __________ a long time__________ two days __________ 1982__________ yesterday evening __________ two weeks__________ I came here __________ two years ago__________ last Sunday __________ last month forforforforforsincesincesincesincesincesincesince2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去现在完成时表“延续”条件一: 与“延续性时间状语”连用现在完成时表“延续”条件二: 谓语要表“延续性”Her parents have married for twenty years. ( )I have bought the pen since a week ago. ( )marry-- be marriedbuy-- have现在完成时表“延续”条件二: 谓语要表“延续性”动词按持续时间分类:瞬间动词& 延续动词如:start, finish, buy, borrow, lend, die, come, go, arrive, leave...瞬间动词不能跟时间段 His grandfather has died for 6 years.如:read, watch, learn, work, stand, know, walk, wait, live, stay... 现在完成时 使用语境1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去We've already finished our homework.Tintin has been popular for over eighty years.时间标志词:before, already, ever, never, yet, so far, up to now... 现在完成时表“延续”条件一: 与“延续性时间状语”连用现在完成时表“延续”条件二: 谓语要表“延续性”瞬间动词转化为延续动词for+段时间,since + 点时间现在完成时 Vs. 一般过去时模糊时间 Vs. 确切过去时间1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响 have/ has + p.p. (过去分词)We finished our homework two hours ago.We've already finished our homework.现在完成时一般过去时确切过去时间言外之意:我们该放松一下了。 现在完成时 Vs. 一般过去时 模糊时间 Vs. 确切过去时间模糊时间1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响I have watched the Youth With You before.I watched the Youth With You yesterday evening.言外之意:我早就看过了。时间标志词:before, just, already, ever, never, yet, so far, up to now... 现在完成时模糊时间一般过去时确切过去时间
时态讲解一般现在时主要用动词原形表示,如果主语是第三人称单数则在动词原形后加s或es。动词第三人称单数的构成方式如下: 一般现在时经常性或习惯性的动作或状态考点突破客观事实或普遍真理The earth goes around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。主将从现(时间、条件、让步)If it rains tomorrow,we won’t/ will not go to the park. When I grow up,I will go to America.Although he is 14 years old, he will join the army. 常与often,always总是,usually,sometimes,once a week,every day等表示频率的副词或时间状语连用。如:I often go to school by bike. ( )1. If Nancy the exam,she will go to Australia for English study. A.pass B.passed C.passes D.will pass ( )3. — I don’t know if Mr.Li to the party this evening. —I think he will come if he free. A.will come; is B.will come; will be C.comes; is D.comes; will beC A( )2. The Greens will visit Hainan as soon as they to China. A.comes B.come C.came D.will come( )4. Now my father his bike to work every day instead of driving. A.Ride B.rode C.rides D.will rideBC一般过去时用动词的过去式表示,即:主语+动词的过去式。动词过去式和过去分词的变化分为规则和不规则两种。下表是动词的过去式和过去分词的变化规则:一般过去时过去发生的动作或存在的状态考点突破常与last night昨晚,yesterday,last week上周,some years ago,in 1995,in the past在过去,the other day几天以前,at that time, 在那时候,在那个时刻,just now等表示过去的时间状语连用。如: I got up at six yesterday. 过去的习惯或经常发生的动作When I was in the countryside乡下,I often swam in the river.主句现在完成时,since从句一般过去时He has worked in the factory since it opened in 1990.You haven’t changed much since we last met.grow -- grewknow -- knewthrow -- threwblow -- blewwrite -- wrotedrive -- drove ride -- rodeget -- gotforget -- forgotlend -- lentsend -- sentspend -- spentsay -- said pay -- paidstand -- stoodunderstand – understood明白let -- let put -- putcut -- cut read -- read*am, is -- was are -- were do -- did go -- went have -- hadsee -- sawcan -- couldmay -- mightdig – dug挖掘eat -- atefind -- foundmake -- madehear -- heardrun -- rantake -- tookhold – held举行,拿着speak -- spokeleave -- leftkeep -- keptsleep -- sleptsweep -- swepttell -- toldsell -- soldbegin -- begansing -- sangsit -- satswim -- swamring -- ranggive -- gave bring -- broughtbuy -- boughtthink -- thoughtteach -- taughtcatch -- caughtcome -- came become -- became ( ) 1. Our math teacher in our school for 20 years and he_____ here when he was 23 years old. A.has taught;has come B.taught;comes C.taught;came D.has taught;came ( ) 2. — You have found your lost umbrella, haven’t you? —Yes.I it behind the door this afternoon. A.have found B.will find C.found D.find DC一般将来时通常用“主语+will/ shall/be going to+动词原形”来表示,有些动词可以用“主语+be doing”形式来表示。 一般将来时肯定句:主语 + will / shall + 动词原形否定句:主语 + will / shall not + 动词原形一般疑问句:Will + 主语 +动词原形?特殊疑问句:W、H开头特殊疑问词 +一般疑问句?肯定/否定回答: Yes,主语+will. /No,主语+will not.will not=won’t将来发生的动作或存在的状态考点突破常与tomorrow,next week,in a few days(在一些天以内),next Sunday等表示将来的时间状语连用。如:Will you be back in two days?be going to+动词原形,表示打算做某事,常指已经决定的、很可能发生的事或有某种迹象表明要发生的事What are you going to do next Sunday? be doing也可表示即将发生或安排好要做的事情常用这种结构的动词有:go,come,leave,arrive,start,begin等。如:She is going there tomorrow.详写内容……点击输入本栏的具体文字,简明扼要的说明分项内容,此为概念图解,请根据您的具体内容酌情修改。详写内容……点击输入本栏的具体文字,简明扼要的说明分项内容,此为概念图解,请根据您的具体内容酌情修改。点击输入内容点击输入内容易错点:There be 句型的一般将来时There will beThere won’t beWill there be…?Yes,there will.No,there will not.There is/are going to beThere is/are not going to beIs/Are there going to be…?Yes,there is/are.No,there is/are not.There will be a football match tomorrow.There is going to be a football match tomorrow.( )1. —Let’s go fishing if it this weekend. —But nobody knows if it . A.is fine;will rain B.will be fine;rains C.will be fine;will rain D.is fine;rains ( )2. If there is any change to the plan, I you as soon as possible. A.told B.have told C.tell D.will tell AD现在进行时的构成为:主语+be(am/is/are)+动词的现在分词。动词的现在分词和动名词的变化规则如下表: 现在进行时表示此时此刻正在进行的动作考点突破—What are you doing? 你在干什么? —I’m reading English. 我在读英语。表示现阶段正在进行的动作或存在的状态I’m reading books these day.while从句动词通常要用进行时While you are sitting on the grass,I’ll read you the novel.现在进行表将来come, go,leave,arrive,start等动词用现在进行时表示将来。如:The bus is coming soon. ( ) 1. Don’t disturb Allen now. He _____ for the Spelling Bee competition.A.prepares B.prepared C.is preparing D.will prepare( )4. Be quiet ! The students _____ a physics test in the next room.A.had B.have had C.were having D.are having CD( )2. —Alan,it’s late.Why not go to bed? —Jenny hasn’t come back yet.I for her. A.waited B.have waited C.am waiting D.was waiting ( )5. Listen! The phone .Please go to answer it. A.rings B.is ringing C.rang D.will ringCB( )3. —Jackson,I haven’t seen you these days. —I for the coming English test. A.am preparing B.will prepare C.prepare D.have prepared ( )6. —Where’s your mother,Jack? — She’s gone to the supermaket.I think she now. A.shops B.will shop C.shopped D.is shoppingAD2.过去进行时的用法 (1)表示在过去的某个时刻、正在进行的动作或存在的状态或过去某段时间一直做的动作,常与this time yesterday,at that time,at 9:00 last Sunday morning,all night等表示过去的时间状语连用。如: —What were you doing this time yesterday? 昨天的这个时候你在做什么? —I was watching TV. 我在看电视。 过去进行时1.过去进行时的构成 过去进行时的构成为:主语+be(was/were)+doing过去进行时。 (2)表示一个过去的动作发生时或发生后,另一个过去的动作正在进行。过去进行时也可用来表示过去一段时间内持续发生的动作。如:When I was watering the garden,it began to rain. While we were having a party,the lights went out. (3)表示两个过去的动作同时进行,这时可用连接词while连接。如: I was writing while my mother was cooking.George was reading while his wife was listening to the radio. (4)“was going+动词不定式”表示过去打算做某事。如: He was going to be our team leader.( )1.— I didn’t see you at the beginning of the party last night. —I on my biology report at that time. A.worked B.work C.was working D.am working( )4 .— Why didn’t you go to the cinema with us this afternoon? — I at the station for my uncle from Beijing. A.was waiting B.have waited C.am waiting D.will wait CA( )2. Jenny in the kitchen when you called her at 5 o’clock this afternoon. A.is cooking B.was cooking C.cooks D.cooked( )5. — I called you at 4:00 yesterday afternoon, but no one answered. —Sorry, I with my friends at that time. A.swim B.swam C.will swim D.was swimmingBD( )3. Louis computer games when her brother phoned her. A.plays B.is playing C.has played D.was playing( )6. I was very angry with John, he just when I spoke to him. A.isn’t listening B.hasn’t listened C.didn’t listen D.wasn’t listening DD现在完成时用法:表示过去发生的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,强调的是现在的情况。构成:助v. have/has + done否定句:haven’t / hasn’t + done一般疑问句:Have / Has sb. done…?I have... = I've You have... = You've...We have... = We've... They have... = They've...He has... = He's... She has... = She's缩写形式: have/ has + done. (过去分词)过去分词不规则变化 现在完成时 使用语境1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去We've already finished our homework.Tintin has been popular for over eighty years. have/ has + done. (过去分词)2.常用标志词: already(肯定句) yet(否定句和疑问句 句末)never(否定句)ever just before(句末)so far, these days, 1.She has not seen this film . She has seen this film.2.I have combed my hair. Have you combed your hair .3.He has watched a video. He has not watched a video . already ---------- yet 已经 用于肯定句 用于否定句,疑问句 yetalreadyalready yet yet already3.对点练习:1. I ________ (do) my homework already.2. He _____________(not finished) his homework yet.3. _______you ever ______ (be) to Haiwaii?4. We ______ never ______ (see) such an exciting match before.5.Mother _____ just _______(clean) the house. Please don’t come in.6.They _________________(practice) this dialogue twice.have donehas not finishedHavebeenhaveseenhascleanedhave practiced1. have been to +地名, “曾经去过某地”, 人已回来 They have been to Beijing twice. 2. have gone to +地点, “去了某地”, 人未回来 They have gone to Beijing. 3. have been in +地点, “在某地待了多久”,可以和时间段连用 They have been in Beijing for 10 years. 4.【特殊句型要牢记】 用have /has been to和have / has gone to have been in 填空 1.Lucy has been to the Great Wall twice. 2.— What about your sister,Lily? — Oh,she Chengdu, she will come back next week.3.The Blacks have been in China for two years. has gone to2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去现在完成时表“延续”条件一: 与“延续性时间状语”连用Tintin has been popular for over eighty years.Tintin has been popular since 1929.Tintin has been popular since over eighty years ago.Tintin has been popular since the artist invented him.“延续性时间状语”: for + 时间段 since + 时间点Have a Try: 用 for 和 since 填空__________ three minutes __________ a week__________ two o'clock __________ a long time__________ two days __________ 1982__________ yesterday evening __________ two weeks__________ I came here __________ two years ago__________ last Sunday __________ last month forforforforforsincesincesincesincesincesincesince2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去现在完成时表“延续”条件一: 与“延续性时间状语”连用现在完成时表“延续”条件二: 谓语要表“延续性”Her parents have married for twenty years. ( )I have bought the pen since a week ago. ( )marry-- be marriedbuy-- have现在完成时表“延续”条件二: 谓语要表“延续性”动词按持续时间分类:瞬间动词& 延续动词如:start, finish, buy, borrow, lend, die, come, go, arrive, leave...瞬间动词不能跟时间段 His grandfather has died for 6 years.如:read, watch, learn, work, stand, know, walk, wait, live, stay... 现在完成时 使用语境1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响2. 动作开始于过去某一刻,一直持续到现在,并可能继续下去We've already finished our homework.Tintin has been popular for over eighty years.时间标志词:before, already, ever, never, yet, so far, up to now... 现在完成时表“延续”条件一: 与“延续性时间状语”连用现在完成时表“延续”条件二: 谓语要表“延续性”瞬间动词转化为延续动词for+段时间,since + 点时间现在完成时 Vs. 一般过去时模糊时间 Vs. 确切过去时间1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响 have/ has + p.p. (过去分词)We finished our homework two hours ago.We've already finished our homework.现在完成时一般过去时确切过去时间言外之意:我们该放松一下了。 现在完成时 Vs. 一般过去时 模糊时间 Vs. 确切过去时间模糊时间1. 动作在过去发生,并且已经结束,但是对现在产生了影响I have watched the Youth With You before.I watched the Youth With You yesterday evening.言外之意:我早就看过了。时间标志词:before, just, already, ever, never, yet, so far, up to now... 现在完成时模糊时间一般过去时确切过去时间

相关资料
更多









