中考英语语法一轮复习——八大时态(无答案) 教案
展开初中英语八大时态(讲与练)
(一)谓语动词的形式:
英语的时态是通过谓语动词的变化来体现的。因此,了解谓语动词的形式及其变化规律非常重要。
英语的实义动词有以下五种形式:
(1) 动词原形:动词原形在句子中形式不变。主要用于主语为第一、二人称的一般现在时,情态动词之后,或根据语法规定必须用动词原形的其他情况。
(2) 一般现在时第三人称单数形式(简称现单三):主要用于主语为第三人称单数的一般现在时。
(3) 过去式:主要用于一般过去时。
(4) 现在分词:主要用于进行时态。
(5) 过去分词:主要用于完成时态,或被动语态。
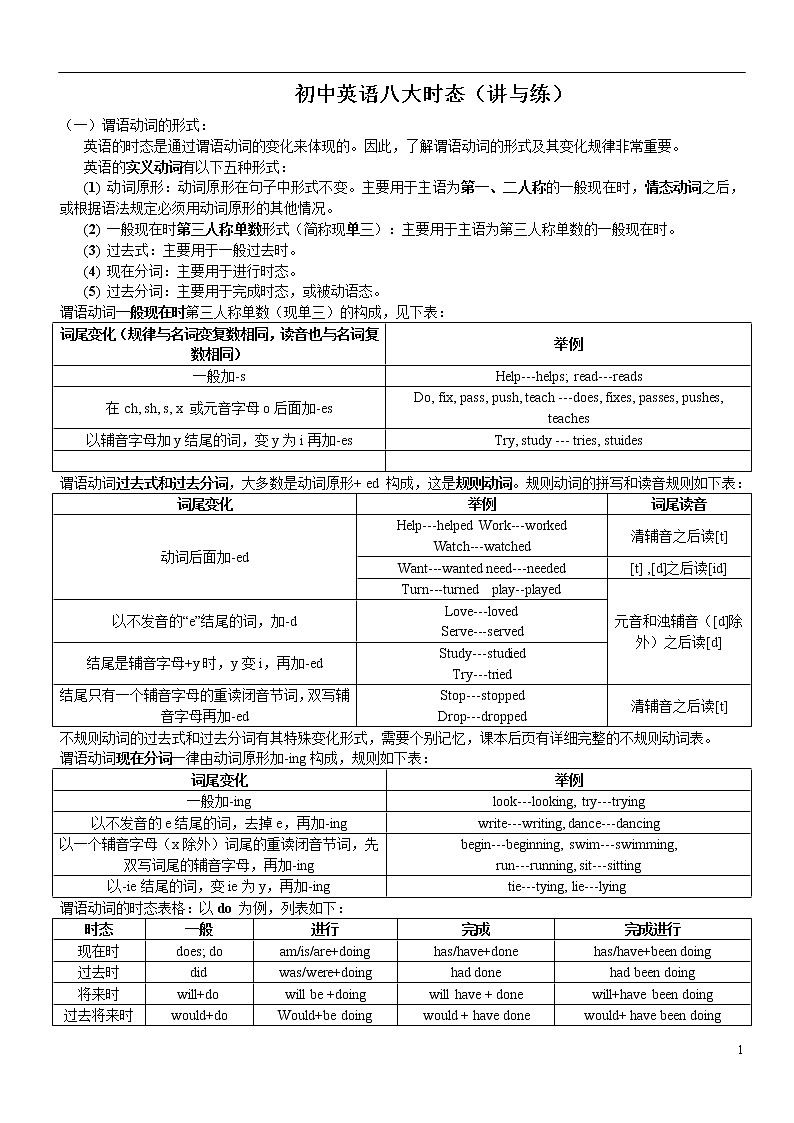
谓语动词一般现在时第三人称单数(现单三)的构成,见下表:
词尾变化(规律与名词变复数相同,读音也与名词复数相同) | 举例 |
一般加-s | Help---helps; read---reads |
在ch, sh, s, x 或元音字母o后面加-es | Do, fix, pass, push, teach ---does, fixes, passes, pushes, teaches |
以辅音字母加y结尾的词,变y为i再加-es | Try, study --- tries, stuides |
|
|
谓语动词过去式和过去分词,大多数是动词原形+ ed 构成,这是规则动词。规则动词的拼写和读音规则如下表:
词尾变化 | 举例 | 词尾读音 |
动词后面加-ed | Help---helped Work---worked Watch---watched | 清辅音之后读[t] |
Want---wanted need---needed | [t] ,[d]之后读[id] | |
Turn---turned play--played | 元音和浊辅音([d]除外)之后读[d] | |
以不发音的“e”结尾的词,加-d | Love---loved Serve---served | |
结尾是辅音字母+y时,y变i,再加-ed | Study---studied Try---tried | |
结尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节词,双写辅音字母再加-ed | Stop---stopped Drop---dropped | 清辅音之后读[t] |
不规则动词的过去式和过去分词有其特殊变化形式,需要个别记忆,课本后页有详细完整的不规则动词表。
谓语动词现在分词一律由动词原形加-ing构成,规则如下表:
词尾变化 | 举例 |
一般加-ing | look---looking, try---trying |
以不发音的e结尾的词,去掉e,再加-ing | write---writing, dance---dancing |
以一个辅音字母(x除外)词尾的重读闭音节词,先双写词尾的辅音字母,再加-ing | begin---beginning, swim---swimming, run---running, sit---sitting |
以-ie结尾的词,变ie为y,再加-ing | tie---tying, lie---lying |
谓语动词的时态表格:以do 为例,列表如下:
时态 | 一般 | 进行 | 完成 | 完成进行 |
现在时 | does; do | am/is/are+doing | has/have+done | has/have+been doing |
过去时 | did | was/were+doing | had done | had been doing |
将来时 | will+do | will be +doing | will have + done | will+have been doing |
过去将来时 | would+do | Would+be doing | would + have done | would+ have been doing |
(二)谓语动词的时态:
“时态”就是通过谓语动词的形态变化,来表达动作发生的时间(现在、过去、将来、过去将来)
及所处的状态(一般、进行、完成、完成进行)。
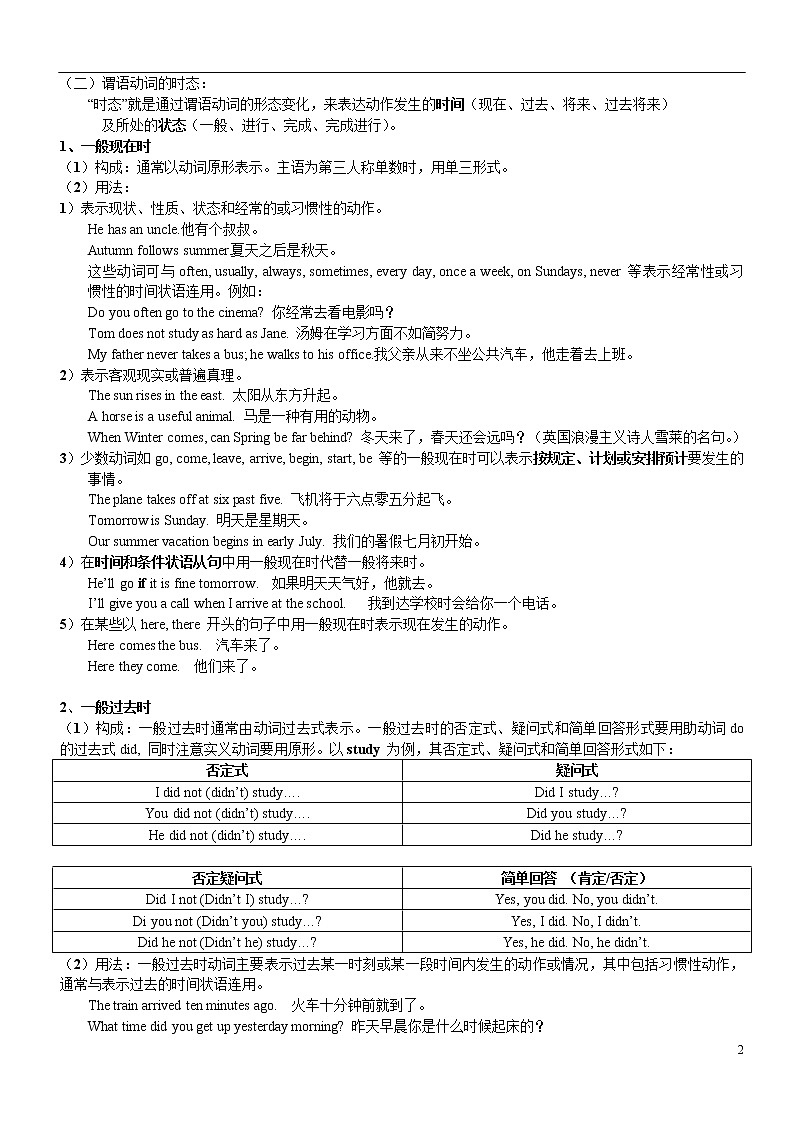
1、一般现在时
(1)构成:通常以动词原形表示。主语为第三人称单数时,用单三形式。
(2)用法:
1)表示现状、性质、状态和经常的或习惯性的动作。
He has an uncle.他有个叔叔。
Autumn follows summer.夏天之后是秋天。
这些动词可与often, usually, always, sometimes, every day, once a week, on Sundays, never 等表示经常性或习惯性的时间状语连用。例如:
Do you often go to the cinema? 你经常去看电影吗?
Tom does not study as hard as Jane. 汤姆在学习方面不如简努力。
My father never takes a bus; he walks to his office.我父亲从来不坐公共汽车,他走着去上班。
2)表示客观现实或普遍真理。
The sun rises in the east. 太阳从东方升起。
A horse is a useful animal. 马是一种有用的动物。
When Winter comes, can Spring be far behind? 冬天来了,春天还会远吗?(英国浪漫主义诗人雪莱的名句。)
3)少数动词如go, come, leave, arrive, begin, start, be 等的一般现在时可以表示按规定、计划或安排预计要发生的事情。
The plane takes off at six past five. 飞机将于六点零五分起飞。
Tomorrow is Sunday. 明天是星期天。
Our summer vacation begins in early July. 我们的暑假七月初开始。
4)在时间和条件状语从句中用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
He’ll go if it is fine tomorrow. 如果明天天气好,他就去。
I’ll give you a call when I arrive at the school. 我到达学校时会给你一个电话。
5)在某些以here, there 开头的句子中用一般现在时表示现在发生的动作。
Here comes the bus. 汽车来了。
Here they come. 他们来了。
2、一般过去时
(1)构成:一般过去时通常由动词过去式表示。一般过去时的否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式要用助动词do 的过去式did, 同时注意实义动词要用原形。以study 为例,其否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式如下:
否定式 | 疑问式 |
I did not (didn’t) study…. | Did I study…? |
You did not (didn’t) study…. | Did you study…? |
He did not (didn’t) study…. | Did he study…? |
否定疑问式 | 简单回答 (肯定/否定) |
Did I not (Didn’t I) study…? | Yes, you did. No, you didn’t. |
Di you not (Didn’t you) study…? | Yes, I did. No, I didn’t. |
Did he not (Didn’t he) study…? | Yes, he did. No, he didn’t. |
(2)用法:一般过去时动词主要表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间内发生的动作或情况,其中包括习惯性动作,通常与表示过去的时间状语连用。
The train arrived ten minutes ago. 火车十分钟前就到了。
What time did you get up yesterday morning? 昨天早晨你是什么时候起床的?
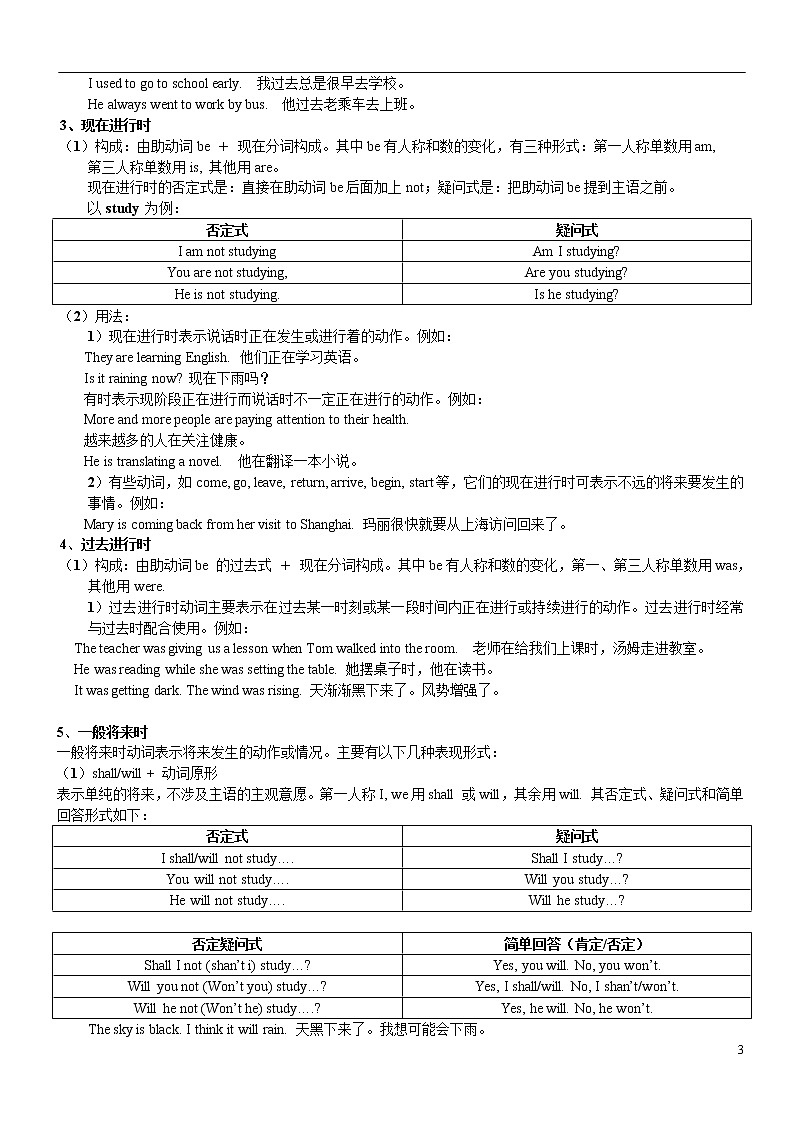
I used to go to school early. 我过去总是很早去学校。
He always went to work by bus. 他过去老乘车去上班。
3、现在进行时
(1)构成:由助动词be + 现在分词构成。其中be有人称和数的变化,有三种形式:第一人称单数用am,
第三人称单数用is, 其他用are。
现在进行时的否定式是:直接在助动词be后面加上not;疑问式是:把助动词be提到主语之前。
以study 为例:
否定式 | 疑问式 |
I am not studying | Am I studying? |
You are not studying, | Are you studying? |
He is not studying. | Is he studying? |
(2)用法:
1)现在进行时表示说话时正在发生或进行着的动作。例如:
They are learning English. 他们正在学习英语。
Is it raining now? 现在下雨吗?
有时表示现阶段正在进行而说话时不一定正在进行的动作。例如:
More and more people are paying attention to their health.
越来越多的人在关注健康。
He is translating a novel. 他在翻译一本小说。
2)有些动词,如come, go, leave, return, arrive, begin, start等,它们的现在进行时可表示不远的将来要发生的事情。例如:
Mary is coming back from her visit to Shanghai. 玛丽很快就要从上海访问回来了。
4、过去进行时
(1)构成:由助动词be 的过去式 + 现在分词构成。其中be有人称和数的变化,第一、第三人称单数用was,其他用were.
1)过去进行时动词主要表示在过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行或持续进行的动作。过去进行时经常与过去时配合使用。例如:
The teacher was giving us a lesson when Tom walked into the room. 老师在给我们上课时,汤姆走进教室。
He was reading while she was setting the table. 她摆桌子时,他在读书。
It was getting dark. The wind was rising. 天渐渐黑下来了。风势增强了。
5、一般将来时
一般将来时动词表示将来发生的动作或情况。主要有以下几种表现形式:
(1)shall/will + 动词原形
表示单纯的将来,不涉及主语的主观意愿。第一人称I, we用shall 或will,其余用will. 其否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式如下:
否定式 | 疑问式 |
I shall/will not study…. | Shall I study…? |
You will not study…. | Will you study…? |
He will not study…. | Will he study…? |
否定疑问式 | 简单回答(肯定/否定) |
Shall I not (shan’t i) study…? | Yes, you will. No, you won’t. |
Will you not (Won’t you) study…? | Yes, I shall/will. No, I shan’t/won’t. |
Will he not (Won’t he) study….? | Yes, he will. No, he won’t. |
The sky is black. I think it will rain. 天黑下来了。我想可能会下雨。
You will meet him at the station this afternoon. 你下午会在车站碰到他。
When shall we see you next time? 我们下次什么时候能看见你呢?
He probably won’t go with us. 他大概不能和我们一起去。
(2)be going + 动词不定式
1)这种结构表示主体现在打算在最近或将来要做某事。这种打算往往是事先考虑好的。例如:
My brother is going to learn English next year. 我哥哥准备明年学英语。
I am going to meet Tom at the station at six. 我六点钟要到火车站去接汤姆。
2)这种结构还可以表示说话人根据已有的迹象认为非常可能即将发生某事。例如:
I think it is going to snow. 我看要下雪。
I am afraid I am going to have a bad cold. 恐怕我要得重感冒。
注意:
1)will 和be going to 都可以表示某种意愿。例如:
I won’t (am not going to) tell you my age. 我不(愿意)告诉你我的年龄。
be going to 和will在含义和用法上略有不同。Be going to往往表示事先经过考虑的打算;will多表示意愿,决心。有时不能互换。例如:
I have bought some bricks and I am going to build a kitchen with them.我买了些砖,我要用它们盖个厨房。(不能用will替换)
Can somebody help me? ?I will. 谁能帮我一些吗?―?我来。(不能用be going to替换)
2)be going to 可用于条件状语从句,表示单纯的将来;will则不能。例如:
If you are going to go to the cinema this evening, you’d better take your umbrella with you. 你若今晚去看电影,最好带着雨伞。
3)be to + 动词原形,表示安排、命令或肯定将会发生的事情;在问句中表示征求意见。如:
You are not to smoke in this room. 你不许在这个房间里抽烟。
TTomorrow is still to come. 明天过了还有明天。
4)be about + 动词不定式。这种结构表示正要、即将发生的事情。例如:
Let’s go in. The class is about to begin. 咱们进去吧。马上开始上课了。
They are about to get married. 他们即将结婚。
一般将来时的关键是记住表示将来的几种句型及其用法。
6、过去将来时
(1) 由should/would + 动词原形构成。第一人称用should; 第二、三人称用would。美国英语所有人称一律用would. should/would 的简略形式为’d, 如I’d, you’d; would not 和should not的简略形式分别为wouldn’t 和shouldn’t.
(2)过去将来时表示从过去某时间看将要发生的事情,多用在宾语从句中。还可以表示过去的倾向或过去经常发生的事情。如:
They asked me if I would go to Guangzhou soon. 他们问我是否很快要去广州。
She told me she would come again next week. 她和我说她下周还来。
(3)其他表示过去将来时的结构:
1)were/was going to + 动词原形,表示过去的安排、打算或确信某事会发生,多用于口语。如:
I told her I was going to see her that afternoon. 我告诉她我那天下午要去看她。
2)were/was to + 动词原形,表示安排,命令或后来将要发生的事。如:
He didn’t know he was to become famous later on. 他不知道以后他会出名。
3)were/was about to + 动词原形,表示正要、即将发生的事。如:
He was about to say something more, but then checked himself. 他正要再说点什么,却又打住了。
He waited until she was about to leave. 他一直等到她即将离开。
7、现在完成时
(1)构成:现在完成时由助动词have + 过去分词构成,助动词have 有人称和数的变化。第三人称单数用has,其余用have.
现在完成时的否定式直接在助动词后面加上not、疑问式是把助动词提到主语之前。以study 为例,其否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式如下:
否定式 | 疑问式 |
I have not (haven’t) studied…. | Have I studied…? |
You have not (haven’t) studied…. | Have you studied…? |
He has not (hasn’t) studied…. | Has he studied…? |
否定疑问式 | 简单回答(肯定/否定) |
Have I not (Haven’t i) studied…? | Yes, you have. No, you haven’t. |
Have you not (Haven’t you) studied…? | Yes, I have. No, I haven’t. |
Has he not (Hasn’t he) studied…? | Yes, he has. No, he hasn’t. |
(2)用法:
1)现在完成时通常强调过去动作或状态对现在的结果或影响。而一般过去时也表示动作已经完成,但强调的是某一动作发生在过去这一事实。例如:
My daughter has just gone out. 我女儿刚出去。
2)表示持续到现在的动作或状态,往往和包括现在在内的表示一段时间的状语连用,如today, these days, recently, now, lately, for…, since…, in the last/past two weeks/years/days/months, just 等。如:
I haven’t heard from her these days. 这些日子我没有收到她的信。
We haven’t seen you recently. 最近我们没有见到你。
She has been with us since Monday.
她从星期一就一直和我们在一起。
注意:
1)表示短暂意义的动词如open, go, come, die, arrive, leave, lose, fall等,在完成时当中不能和包括现在在内的表示一段时间的状语连用,因为它们表示的动作不可能持续。因此,不能说:
×He has come here for 2 weeks.
×The old man has died for 4 months.
以上两句话可以改为:
It’s two weeks since he came here. He has been here for 2 weeks.
It’s 4 months since the old man died.
2)have (has) been 和have (has) gone的区别:表示“曾到过某地”要用 “have (has) been”; 表示“已经去某地”要用 “have (has) gone”。试比较:
They have been to Canada. 他们到过加拿大。(现在已经不在加拿大)
They have gone to Canada. 他们到加拿大去了。(可能在路上和已经到加拿大).
8、过去完成时
(1)构成:一律用had + 过去分词构成。
(2)用法:
1)表示发生在过去某一时间或动作之前的事情,即“过去的过去”。用过去完成时,必须有一个过去的时间或动作来作参照,说明在此之前某事已发生。如果两个动作都是在过去发生的,先发生的用过去完成时,后发生的用一般过去时。例如:
She told me she had been there three times before. 她告诉我她以前到过那里三次。(“去过”发生在“告诉”之前)
How long had he taught here by the end of last term? 到上学期末为止,他在这里教学多长时间啦?
When we arrived, the football match had already begun. 我们到的时候,足球赛已经开始了。
2)过去完成时动词可以表示过去某一时刻之前发生的动作或呈现的状态,这一动作一直持续到过去这一时刻或将继续下去。
By six o’clock they had worked for eight hours. 到六点为止,他们已工作八小时了。
When I came to Shanghai, he had been there for a long time. 我到上海时,他在那里很长时间了。
时态综合练习
(一)用一般现在时或现在进行时填空
- Look! It ________(rain). It seldom ________(rain) this time.
- Bill Gates _________(use) this computer, but he __________(not use) it at the present.
- Don’t be late, Jane; the train ________(start) at six in the morning.
(二)用一般现在时或一般将来时填空
- I don’t know when Bob _________(return), but when he ________(return)
I ________(let) you know.
5. We _______(send) for a doctor if you ________(be) not better this afternoon.
6. The plane ______(be) about to take off. ______ he _______(get) to the airport in time?
7. I’m sure the harder you _______(work), the better progress you __________(make).
(三)用一般过去时或过去进行时填空
8. The fireman ______(go) towards the fire, which ______ still _______(smoke).
9. While my father ________(look) through the evening paper, he suddenly _____(let) out
a cry of surprise.
10. When I _______(enter) the classroom, she _______(not see)me, for she ______(read) a novel.
11. When they _______(arrive) at the village, it ________(get) dark, and the wind _______(blow) hard.
12. I _______(not know) both of you _________(wait) for me here.
(四)用一般过去时或过去将来时填空
13. In her letter, she _______(tell) me that she _______(take) the entrance examination this year.
14. I _________(not expect) that so many people _________(come) to the party.
15. He said that he ________(not go) with us if he ______(be) too busy.
16. They promised that they _________(bring) us all the necessary books as soon as they ______(have) a chance.
17. ----- ________(do) your brother come back the other day? -----No. He said he _________(come) back in two days.
(五)用一般过去时或现在完成时填空
18. ----I can’t find my glasses. _______ you ______(see) them?
----Yes, You _______(leave) them in the car yesterday.
19. The tape recorder ______(be) out of order last week. We ______(have) it repaired the day before yesterday. It ________(be) in good condition ever since.
20.---- How _______you _____since I ______(see) you last?
---- Very well, thank you. And you?
21. It _____(be) ten years since we ______(part).
22. -----I _________(not see) you for ages! Where ______ you ______(be)?
-----I _______(be) to Scotland.
23. I can’t lock the door. I _________(lose) my key. I_____(lose) it while I _____(be) out.
24. We _______(know) each other since we ______(be) boys.
25. You _________(not do) what you _______(promise) to do.
(六)用一般过去时或过去完成时填空
26. The solider _______(die). A bullet _______(pass) through his chest.
27. The task _______(be) much harder than we __________(expect).
28. Mr. Hu _________(not feel) so well, as he _________(catch) a bad cold.
29.The hero _______(give) a gold medal for what he_______(do) for his country.
30. I __________(cannot go) out that night, for I ________(promise) to wait for Mary at home.
31. We ________( not know) you _______(be) so busy in the past two years.
32. Mother ______ hardly _______(reach) home when it _______(begin) to rain.
(七)用现在完成时或现在完成进行时填空
33.----I am sorry I ________(kept) you waiting so long.
-----It is all right. I __________(read) the newspaper.
34. The CCTV _________(broadcast) English programmes ever since 1977.
(八)时态综合填空
35. You ______(feel) better when you ______(take) the medicine.
36. She said we _________(may keep) the book as long as we ______(like).
37. Please wake me up if I _____ still ______(sleep) when you _______(come) home.
38. My sister ___________(learn) English since she ______(be) a child. She ______(speak) English very fluently now.
39. My uncle _______(come) to see us. He _______(arrive) here a few days ago. He ______(leave) for Sydney tomorrow morning.
40. He ______(break) his leg when he _________(play) in a football match against another school.









